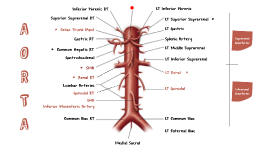
Aorta
Transcript: Bicuspid Valve any of the tubes forming part of the blood circulation system of the body, carrying in most cases oxygen-depleted blood TOWARD the heart essentially tubes that collapse when their lumens are not filled with blood Veins are less muscular than arteries and are often closer to the skin valve between the left atrium and the left ventricle is an aortic valve that only has two leaflets, instead of three regulates blood flow from the heart into the aorta, the major blood vessel that brings blood to the body Veins one of the heart valves first one that blood encounters as it enters the heart stands between the right atrium and the right ventricle it allows blood to flow only from the atrium into the ventricle Pictures! (: Vena Cava chamber in the heart that is responsible for pumping deoxygended blood to the lungs located in the lower left portion of the heart below the right artium and opposite of the left ventricle As deoxygenated blood flows into the right atrium, it passes through the tricuspid valve and into the right ventricle, which pumps the blood up through the pulmonary valve and through the pulmonary artery to the lungs artey that supplies blood to the heart called the coronary arteries because they encircle the heart in the manner of a crown run along the outside of the heart and have small branches that dive into the heart muscle to bring it blood Intresting Facts about the Circulatory System Aorta Tricuspid Valve vein carrying oxygenated blood from the lungs to the left artium of the heart one of the four vessels that carry aerated blood from the lungs to the left artium of the heart only veins that carry bright-red oxygentated blood The Circulatory System Right Ventricle left lower chamber of the heart, below the left artium receives blood from the left artium and pumps it out under pressure through the aorta to the body separated by the mitral valve as the heart contracts, blood will flow back into the left atrium, and then through the mitral valve, where it next enters the left ventricle Right Atrium Left Ventricle Pulmonary Vein If you were to lay out all of the arteries, capillaries and veins in one adult, end-to-end, they would stretch about 60,000 miles (100,000 kilometers) Capillaries are tiny, averaging about 8 microns (1/3000 inch) in diameter, or about a tenth of the diameter of a human hair An adult human has an average resting heart rate of about 75 beats per minute, the same rate as an adult sheep the ancient Egyptians were cardiocentric — they believed the heart, rather than the brain, was the source of emotions, wisdom and memory, among other things After circulating within the body for about 120 days, a red blood cell will die from aging or damage any of the muscular-walled tubes forming part of the circulation system by which blood (mainly that which has been oxygenated) is carried away from the heart to all parts of the body blood in arteries is usually full of oxygen, the hemoglobin in the red blood cells is oxygenated. The resultant form of hemoglobin (oxyhemoglobin) is what makes the arterial blood look bright red The Human Heart - Main Parts main artery of the body supplies oxygenated blood to the circulatory system in humans, it passes over heart from the left ventricle and runs down in front of the backbone is a tube that is about a foot long and is just about 2 inches long Like all arteries, the aorta's wall has several layers: The intima, the innermost layer, provides a smooth surface for blood to flow across. The media, the middle layer with muscle and elastic fibers, allows the aorta to expand and contract with each heartbeat. The adventitia, the outer layer, provides additional support and structure to the aorta artery that carries blood from the right ventricle of the heart to the lungs for oxygenation this is the last segment of a long journey for circulating blood known as pulmonary trunk, which is relatively short and wide branches off in two directions -- the left & right pulmonary artery Arteries one of the four chambers of the heart hollow structure deoxygenated blood enters the right atrium through the inferior and superior vena cava located in upper right corner above the right ventricle largest vein in the body carries deoxygenated blood into the heart There are two in humans, the inferior vena cava (carrying blood from the lower body) and the superior vena cava (carrying blood from the head, arms, and upper body) Pulmonary Artery Coronary Vessels