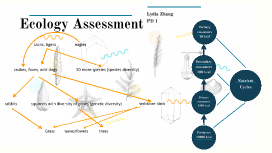
Ecology Assessment
Transcript: The Elephant Abiotic/biotic factors Elephantidae (scientific name) are the largest living land animal and have distinctly massive bodies, large ears and long trunks. Elephant ansetory spans over 56 million years and inculdes more than 300 proboscidean spices. Elephants belong to the genus Elephas which inculdes two living species. The African Elephant (Elephas maximas) and the Asian Elephant (Elehas maximus). The closest living thing to an Elephant are Hyraxes,.This is because Elephant and Hyraxes both descended from a common ancestor the Tethythera, who died out some 50 million years ago. But the closest non-living thing to and elephant is the Wooly Mammoths. At the morphological level the Wooly Mammoth has most often considered as the sister spieces of Asian elephants, and the two mammals share a 99.6 similar DNA makeup. Some abiotic factors of the Elephant inculde temperture, rainfall, soil compostion, and availbitly of water sources.These factors can influence the distribution, behavior, and survival of the Elephants in their habitat. For example Elephants require access to water for drinking and bathing, so the availability of water sources is crucial for their well being. Changes in temperature and rainfall patterns can also affect the availability of food and water, which can have an impact on elephant populations. Some biotic factors related to elephants inculde their interactions with other species, such as predators, prey and symbolic relationships. Predators like lions and tigers can pose a threat to Elephants, while their interaction with herbivores like zebras and antelopes can influence competition for resources. Elephants also have symbolic relationships with certain birds and certain insects, such as oxpeckers and beetles, which help remove parasites from their bodies. These biotic factors play a role in shaping the dynamics of elephant populations and their overall ecosystem. Ecological Niche The ecological niche of an elephant can be described as a large herbivorous mammal that plays a vital role in shaping its ecosystem. As primary consumers, Elephants have a significant impact on vegetation through their feeding habits, which can infuence plant growth and distribution. They aslo act as seed dispersers, helping to disperce seeds through their dung. Also, Elephants create water hole by clearing pathways in their habitat, benefiting other species by providing access to water and creating new opportunities for movement. Overall, Elephants are considered keystone species. Habitat Adaptations Elephants are found most often in savannas, grasslands, and forests. But they occupy a wide range of habitats, including deserts, swamps, and highlands in tropical and subtropical regions of Africa and Asia, this is becuase Elephants are higly adaptable and can be found in both wet and dry envirments. Elephants require access to water sources for drinking and bathing, so they are often found near rivers, lakees or watering holes. They prefer areas with a lot of vegetation for grazing and browsign on leaves, grasses and other plant materials. the diverse habitats elephants occupy reflect their ability to thrive in different ecosystems around the world. A few of the websistes I used where National Geographic, and World Wildlife fund. Elephants have many strucatural adaptations. For example their long tusks are actually enlongated incisor teeth, which they use for various tasks like digging, fighting, and gathering food. Their strong muscular trunks are incredibly versatile, allowing them to grasp objects, drink water, and even communicate through touch and sound. Also, their thick wrinkled skin helps protect them from the sun and insect bites. Some behavioral adaptations Elephants have is they live in tight-knit social group called herds, where they communicate through a variety of different vocalizations, body lanuage, and even infrasound which is a low frequency sound that can travel long distances. They aslo has remarkable memory and intelligence, allowing them to remember important locations, navigate their enviroment, and learn from eachother. Elephants are also known for their strong maternal instincts and cooperative behavior, often helping eachother in times of need. Elephants have several physiological adatations that help them survive in their enviroment. For example, thier size. Their size helps them intimidate perdators and access food sorces that other animals can't reach. They also have a unique digestive system that allows them to effciently break down and extract nutrients from tough plant materials. Also, Elephants have specialized teeth called molares that continuously grow and relpace worn out ones troughout their lives. These adaptations are able to help them thrive in their enviroment. Elephant