Nutrition Powerpoint
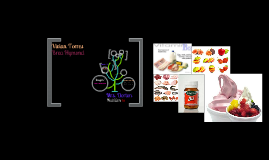
Transcript: Vivian Torres Brea Hymond Vitamin B12 Function Helps to form myelin, which is a fatty cover that insulates your nerves. * Helps to produce energy from metabolism of fat and protein. * Helps to produce hemoglobin, which is the component of your red blood cells that carrys oxygen to your cells. This is why a vitamin B12 deficiency can cause fatigue. * Reduces your homocysteine level, which lowers your risk of stroke, heart disease, cancer, Parkinson's, Alzheimer's disease, and many degenerative diseases. * Regulates growth, maintenance, and reproduction of all of your cells Signs of Deficiency Chronic fatigue - macrocytic / megaloblastic anemia Unexplained numbness or tingling of arms or legs Anxiety and irritability Depression Digestive problems like a sore tongue, loss of appetite, and constipation Poor hair muscle weakness, shortness of breath, dizziness, numbness, heart palpitations, bleeding gums and mouth sores, nausea, poor appetite and diarrhea. Vitamin B-12 Gives You . Increased energy Restored mental clarity, and help with memory loss Reduced daily stress and irritability And many other great health benefits What foods provide vitamin B12? Mollusks, clam, mixed species, cooked Liver, beef, braised Fortified breakfast cereals Trout, rainbow, wild, cooked Salmon, sockeye, cooked Trout, rainbow, farmed, cooked Beef, top sirloin, lean, choice, broiled Fast Food, Cheeseburger, regular, double patty & bun Fast Food, Taco, 1 large Fortified breakfast cereals Yogurt, plain, skim Haddock, cooked Clams, breaded & fried Tuna, white, canned in water, drained solids Milk Pork, cured, ham, lean only, canned, roasted Egg, whole, hard boiled American pasteurized cheese food Chicken, breast, meat only, roasted What Is Vitamin B12? Vitamin B12 is also called cobalamin because it contains the metal cobalt. This vitamin helps maintain healthy nerve cells and red blood cells . It is also needed to help make DNA, the genetic material in all cells . Vitamin B12 is bound to the protein in food. Hydrochloric acid in the stomach releases B12 from proteins in foods during digestion. Once released, vitamin B12 combines with a substance called gastric intrinsic factor . This complex can then be absorbed by the intestinal tract. Are there any risks associated with too much vitamin B12? Vitamin B12 is considered safe and non-toxic . Why is vitamin B12 necessary? Knowing the facts about vitamin B is vital for healthy cells: vitamin B12 affects the development and maintenance of red blood cells, nerve cells, and normal myelination (covering) of nerve cells. It also aids in the production of DNA and RNA, and the production of neurotransmitters. " Slogan " Vitamin B12 fills you up inside. Mrs. Dorton Nutrition P2