North Korea Presentation
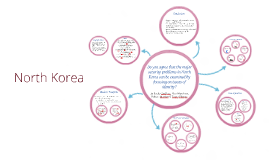
Transcript: “Since 1990 the number of North Koreans fleeing the Democratic People’s Republic of North Korea (DPRK or North Korea) has escalated. Approximately thirty thousand to fifty thousand North Koreans are estimated to have migrated to China. At the end of May 2010 the number of North Koreans currently residing in South Korea had risen to nineteen thousand” (Lee & Kim 2011, p. 59) Perspectives on migration North Korea China South Korea Future problems of migration Security issue for both North Korea and the International Community. Contradicts International Treaties Increases risk of a Security Dilemma and Nuclear War Admittance by Kim Il Sung in 2002 Identity theft for North Korean agents, Forcing the abducted to train agents how to act 'Japanese' Fate of hostages has become a key political point for the Japanese government. Food Crisis The most pressing human security area in North Korea? Economic Crisis “The North Korean economy is one of the world’s most isolated and bleak. It was completely bypassed by the “economic miracles” of the past quarter century that brought modern economic growth and industrialization to South Korea, Taiwan, Singapore and Hong-Kong” (Kihl & Kim, 2006, p.119) North Korea : Focus is on settlement of the past in the form of reparation. It views the hostage situation as resolved. BBC World Service Poll (2013 :35): 92% of Japanese hold a negative view of the DPRK, and no respondents expressed a positive view. This is the most negative outlook in the survey, with the global average at 54% negative, 18% positive, and 28% neutral Do you agree that the major security problems in North Korea can be examined by focusing on issues of identity? “The Japanese side regards, in a spirit of humility, the facts of history that Japan caused tremendous damage and suffering to the people of Korea through its colonial rule in the past, and expressed deep remorse and heartfelt apology” South Korea Migration China “Security and insecurity are no longer considered as conditioned only upon geopolitics and military strength, but also on social, economic, environmental and cultural issues” (Burgess, 2008, p.61) Causes of the rise in importance? UN Human Development Report (1994) Constructivism and human security 1910-1945 Lee (2013, p.59) highlights that 50% of Chinese scholars believe a unified Korea will pose a threat to China with reunification, would become nationalistic could ignite territorial claims over "Gan-do", today's Manchuria - as many Koreans see this as their lost territory undermines Chinese nationalism + identity Importance of Japan North Korea Major US ally in the region (Auslin 2011:196) Third largest economy in the world (IMF, 2013) Key player in terms of regional stability Major role in Six Party Talks Stridently anti-proliferation Japanese Hostage Situation Creates the necessary room for the identities and interests of international actors to take a central place in theorizing international relations. North Korea North Korean Nuclear Programme - source of insecurity Reinforced by identity Without WMD "Rogue State" - illegitimate (Becker, 2005,pix) Accumulation of WMD affirms "Roguish identity" - no legitimacy Cyclical relationship (Shearman, 2013, p148) Undermines power of International Community Human Security Issues Japanese Colonial Era Opposition to Japanese rule as a significant source of Korean identity. Personality Cult of Kim Il Sung, Identity - cause of Nuclear Proliferation Juche, self-reliance: central focus of authority on the state (BBC, 2013/Cumings, 2012, p217) Power and Sovereignty key for state legitimacy (Bluth in Shearman, 2013, p147) Withheld by the International Community Aim of Kim regime - gain legitimacy Engage International community through Nuclear Weapons - only source of leverage (Bluth in Shearman, 2013, p146) Environmental Crisis Deforestation Natural Disasters Pollution Personal & Political Security Freedom House Survey North Korea & Japan Why is human security important? Is the claim that significant elements of international relations are historically and socially constructed, rather than consequences of human nature. Food and Economic Crises in North Korea Summary of Human Security Reunification By Becky Godfrey, Alex Morrison, Robert Morten & Torey Pitman Constructivist Theory Human security and the focus on security for the individual Interrelated nature of human security in North Korea Knock on effects Ideology of self-reliance, 'Juche' Colonial era cultural policy designed to "eradicate individual ethnicity of the Korean race" and can be seen as an example of cultural genocide (Matsumura & Ishida 2004) Identity plays a key role in security threats within the whole region Security threats are subjective and depend on how each state constructs its perception of the issues. Domestic identity impacts foreign policy and thus influences perceptions by the international community According to its constitution 'sole legitimate Korea'; unification is its