Food Packaging
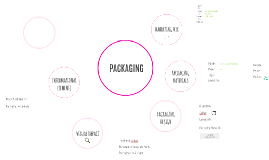
Transcript: FOOD PACKAGING What is food packaging? What is food packaging? Food Packaging is the packaging of the food product, to protect from contamination & damage besides conserving taste & quality during the shelf life of a food product. (Foodsafetyhelpline.com, 2014) The value of packaging produced in Australia is estimated to be approx. $10billion. About 30,000 people are directly employed in the production of packaging in Australia. There are numerous materials used for packaging, the main materials used are plastic, aluminium, paper/board and glass. What packaging is the largest single material used? Materials Materials Glass is the least used out of all 4 materials. It is used mainly for beverages, jams, spreads and preserving perishable foods. Glass containers are used for a variety of reasons: Glass is chemically inert, and does not react with foods to produce flavour changes. It's odourless and hygienic Is usually transparent It's strong and is now being made lighter Is easy to open and reseal Comes in a variety of shapes and size Secures food Glass Glass Metal Metal is one of the cheapest and most widely used types of packaging in Australia, it has decreased over time but is still being used for perishable foods without refrigeration. Aluminium is made up of recycled materials and can be recycled over and over. Manufacturing and selling benefits Two types of cans: Steel cans and aluminium cans Metal/aluminium Plastic Plastic is the second largest sector. It has advantages over other types: It is a more efficient material to choose than alternatives. It's energy efficient to manufacture and is lighter. It can hold a larger amount of liquids compared to aluminium or glass. High resistance to breakage Available in a large variety of colours, shapes and sizes Adds to the sales appeal of the product Plastic Types of plastics Paper/board Paper/board packaging is the largest single material!!! Paperboard packaging comes in several different grades with each having unique characteristics. It is versatile and cost effective. As a manufacturer, you can treat paper to suit the type of product being packed. The most common paper/board used: Solid Bleached Sulfate: Milk and juice gable top cartons/ frozen food packaging/ candy boxes. Coated unbleached kraft paperboard: Frozen food packaging/ beverage cartons and carriers Coated recycled paperboard: Cookie and cracker packaging/ cake mix packaging/ cereal boxes/ dry food packaging Paper/board Food packaging has 5 major functions Functions of packaging The majority of foods need to be put in some sort of container for easy storage and distribution. 1. Packaging contains product. 1. 2. 2. Packaging protects products. Packaging must protect the product from physical and mechanical damage. Consumers tend to avoid damage packaging. Packaging can be damaged through transportation and loading/unloading. Excess moisture and rain will cause irreversible damage to a product. Packaging also protects the food from physical damage during storage within the home. The packaging needs to be able to withstand all possible risks. 3. 3. Packaging preserves foods. All foods are different, so the role of packaging in the preservation of food is quite complex. No single packaging material is able to perform all the following functions. Packaging must: decrease the chances of, or prevent contamination by, micro-organisms that cause food poisoning, especially in dairy foods and seafood prevent moisture entering dry food products prevent loss of moisture from products that contain water allow products such as fresh fruits and vegetables to breathe prevent the process of rancidity of fats, which needs oxygen protect light-sensitive products from ultraviolet light 4. 4. Packaging informs the consumer and promotes the product. The packaging is the only contact between the consumer and the manufacturer. The package: identifies the product and brand displays the quantity and price explains the products features provides directions for use provides health and consumer-protection information required by law (use-by dates, nutritional information, warnings, ingredients list, and the name and address of the manufacturer. 5. 5. Packaging provides convenience. Many packages allow the consumers to use the product directly from the package or save the consumer effort in preparation. Microwaveable meals Whipped cream in a can Sauces/spreads Modern packaging designs allow consumers to use whilst on the go: Salads with forks Yoghurts with spoons Drinkable yoghurts Ring pull cans Labelling Understanding labels on packages can be very confusing and most consumers believe what they read when it says "low fat", but is it low fat? does it have no added sugar? Does this make it healthy? To ensure consumers know exactly what is in the product, they have numerous food standards ( Food Standards Australia and New Zealand) You may also notice home brand products don't have any images on their products as they aren't Due