FMEA
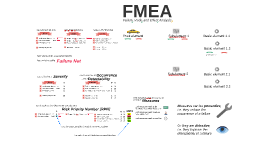
Transcript: There are only 2 essentially different types of FMEA: both types of FMEA require a similar structure starting from here, we'll now only look at the failures Subelement 1 Acceleration takes too long Tooth material too soft Process-centered FMEA Failure Mode and Effect Analysis This is a car. It has several "Functions" - desired characteristics that we expect of it. 8 10 Basic element failures 1 D Diameter < 59.9 mm 8 Severity 4 Torque < 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min S 2 Product-centered FMEA 3 Red and yellow RPNs demand action in form of Car never reaches 100 km/h FMEA Measures Risk Priority Number [RPN] RPN And (you guessed it) it is also done for each basic element, in this example a gearwheel Each Cause has an 3 Occurrence So, for each root in a failure net we can calculate a Root element failures The same is done for each subelement, in this example a motor No means to fix gearwheel on drive shaft & 3 10 Tooth surfaces are too rough Each Effect has a 2 Subelement failures 6 Or they are detective, i.e. they improve the detectability of a failure There seems to be a causal connection... Root element 2 2 Measures can be preventive, i.e. they reduce the occurrence of a failure S O Basic element 2.1 e.g. known as: Design FMEA Machinery FMEA System FMEA Tool FMEA Failures Tooth surfaces are too rough Diameter > 60.1 mm No means to fix gearwheel on drive shaft Tooth material too soft Diameter < 59.9 mm Acceleration takes too long Steering not possible Passengers get wet Car never reaches 100 km/h Basic element 1.1 Tooth surfaces are too rough Diameter > 60.1 mm No means to fix gearwheel on drive shaft Tooth material too soft Diameter < 59.9 mm Basic element 2.2 That's what we call a Failure Net Tooth surfaces are too rough Diameter > 60.1 mm No means to fix gearwheel on drive shaft Tooth material too soft Diameter < 59.9 mm Process FMEA Assembly FMEA Logistics FMEA e.g. known as: Failures Torque < 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min Motor overheats at < 6000 U/min Max power < 150 kW Torque >> 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min Acceleration takes too long Steering not possible Passengers get wet Car never reaches 100 km/h 96 160 24 32 Each measure needs a person responsible for it Subelement 2 Effects Basic element 1.2 The color of the RPN indicates the overall Risk level Functions And for each Function, there is at least one "Failure", a way in which that Function goes wrong Provide a net torque of 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min Ensure safe function up to 6000 U/min Provide up to 150 kW of power Failures Functions And for each Function, there is at least one "Failure", a way in which that Function goes wrong Each measure needs to be clearly defined (when is it over?) Only the worst-case Effect is used for the RPN calculation 4 2 2 2 1 O Each measure needs a deadline Causes Modes Effects Torque < 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min Max power < 150 kW Motor overheats at < 6000 U/min Torque >> 200 Nm @ 3000 U/min ...and a 3 10 1 2 2 D Detectability Acceleration takes too long Passengers get wet Steering not possible Car never reaches 100 km/h Functions And for each Function, there is at least one "Failure", a way in which that Function goes wrong Provide teeth surfaces that can safely transmit 1000 N/tooth to the transmission Provide a means to be fixed on the drive shaft Diameter of force transmission: 60mm +/- 0.1mm Accelerate to 100 km/h in 14s Protect passengers from weather Enable easy steering Causes