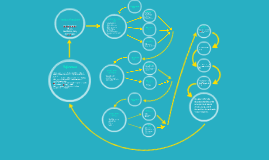
Decision Making Flow Chart
Transcript: One example of a decision that was made at the state level is when the governor of Louisiana, Bobby Jindal tried to pass a bill that authorized the use public monies to fund student vouchers. This would allow parents to pull their student from a failing school and use the voucher to pay for private school. The state legislature agreed and it was signed into law. The law was later challenged and the Louisiana Supreme Court ruled the law unconstitutional )Strauss, 2012,p,1). Had this law not been overturned, it would have greatly affected the states public schools. Public schools would have lost the funding for each student who left with a voucher which would have further depleated their resources making it even harder for them to improve, Example 1 The decisions that mold and shape the educational system in St. Tammany Parish go through many channels before they actually affect the schools. These channels act as filters, which helps ensure that all decisions are well thought through, fair, equitable, and in the best interest of the students. For this system of checks and balances to be effective it is imperative that all members cooperate and collaborate, always having the best interests of the students in mind. Strauss, V. (2012). Louisiana Supreme Court rules school voucher funding unconstitutional. Retrieved from http://www.washingtonpost.com/blogs/answer-sheet/wp/2013/05/07/louisiana-supreme-court-rules-school-voucher-funding-unconstitutional/ St. Tammany Schools: Decisions at the school level Elizabeth Lee EDL/535 March 24, 2014 Rahim Jones Important decision are made everyday that strongly affect the public schools in Louisiana. These decisions are made at three levels: State, District, and School. Every decision is critical to the success of the school and must be carefully weighed and thought through before a decisions are made and policy is enacted. Throughout this presentation we will look at each of the 3 levels and will identify who has decision-making power and responsibilities at each level The principal is responsible for most areas of day-to-day school operation. He/she guides behavior management, budgeting, staff supervision, and curriculum. Principals publicly represent the school and interact with district, state and federal authorities. Vice principals assist the principal in various areas. School Principal Assistant Principal Conclusion Louisiana Department of Education. (2014). About us. Retrieved from http://bese.louisiana.gov/home (Cowen Institute, 2012,p.1) Superintendent of Education St. Tammany Parish School Board School Board Superintendent Assistant Superintendents Board Members State Legislature Governor State administrators Board of Elementary and Secondary Education (BESE) Debates and enacts laws affecting any areas of public education Makes rules that school districts and schools must follow Responsible for funding all pre-k through 12th grade public schools Sets statewide academic standards, testing, and graduation requirements St. Tammany Parish: Decisions at the District Level Example 2 Introduction (Louisiana Department of Education, 2014, p.1) Cowen Institute. (2012). Louisiana K-12 Public Education: Governance, demographics, and enrollment. Retrieved from www.coweninstitute.com/.../2009/08/5-Louisiana-K-12-Education.pdf Another example could include a change that was proposed at the state level for schools to change from iLeap to PARC for standardized testing. This was proposed and voted on by the state, then passed down to the district who was put in charge of implementing it in the schools. The district discussed these changes with the school principals at the monthly meeting and the schools principals are put in charge of preparing their teachers for the upcoming changes. St. Tammany Parish Schools. (2014). School Board. Retrieved from http://stpsb.org/schoolboard.php References Education in Louisiana: A Flow Chart of the Decision Making Process Louisiana: Decisions at the State Level (St. Tammany Parish Schools, 2014, p.1) Local school districts derive their authority from the Legislature. Authorized to levy local property taxes for a particular purpose and negotiate with teachers and other employees over pay, benefits and working conditions. Acts as administrative policy making body for elementary and secondary schools in St. Tammany Parish. Determine staffing levels, curriculum, student assessments, student services and activities, school calendars, school facilities, transportation, and other programs as authorized or required by state law, within the budgetary limits set by the Legislature and local voters.