Cell Division
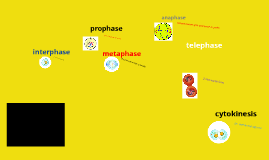
Transcript: - duplicate the DNA within each cell during every cycle of cell division Cytokinesis http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&client=ubuntu&tbo=d&channel=cs&biw=1215&bih=688&tbm=isch&tbnid=Fdk_WHlua4E5bM:&imgrefurl=http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-purpose-of-dna-replication.htm&docid=2ryF_5Hc29UUSM&imgurl=http://images.wisegeek.com/cell-dividing.jpg&w=1000&h=516&ei=_JTGUOLLLoXD2QWPn4CwAQ&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=863&vpy=289&dur=1680&hovh=161&hovw=313&tx=112&ty=94&sig=106767054772201991398&page=2&tbnh=138&tbnw=313&start=29&ndsp=32&ved=1t:429,r:54,s:0,i:249 hh Anaphase http://www.google.com/imgres?imgurl=http://img.sparknotes.com/figures/D/d756b5b73abe2974f3521a828791899f/anaphase.gif&imgrefurl=http://www.sparknotes.com/biology/cellreproduction/mitosis/section2.rhtml&h=327&w=382&sz=13&tbnid=2RPGY6e5kfMoOM:&tbnh=90&tbnw=105&zoom=1&usg=__jPimxpBrZOBOoFdl4JN_vJLV4nE=&docid=1jytR65SCyDfCM&hl=en&sa=X&ei=5JzGUJ6tCsfQqAG_84DIBA&sqi=2&ved=0CEEQ9QEwAw&dur=247 - The chromosomes begin to stretch out and lose their rod like appearance. This occurs in the two regions at the ends of the cell. A new nuclear membrane forms around each region of chromosomes. - each identical rod, or strand of chromosome - they separate from each other and move to opposite ends of the cell DNA Ladder- Deoxyribose and Phosphate How the cell grows and matures Chromosomes and Chromatids http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&client=ubuntu&sa=X&tbo=d&channel=cs&biw=1215&bih=688&tbm=isch&tbnid=EFbK86QK7y2QgM:&imgrefurl=http://www.macroevolution.net/sister-chromatids.html&docid=Rwc9MbyenRNauM&imgurl=http://www.macroevolution.net/images/sister-chromatids-275px.jpg&w=274&h=362&ei=OpfGUOCNE8-yqQHkg4GYCQ&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=245&vpy=129&dur=108&hovh=258&hovw=195&tx=83&ty=107&sig=106767054772201991398&page=1&tbnh=135&tbnw=102&start=0&ndsp=31&ved=1t:429,r:1,s:0,i:113 - During cytokinesis, the cytoplasm divides, distributing the organelles into each of the two cells - what a DNA molecule is most often called based on its twisted ladder like shape Metaphase A cell dividing into two daughter cells. Double Helix Chapter 2.5 Cell Cycle of Mitosis Nitrogen Bases Telophase http://www.google.com/imgres?start=27&num=10&hl=en&client=ubuntu&tbo=d&channel=cs&biw=1215&bih=688&tbm=isch&tbnid=b93W76JGXDhGTM:&imgrefurl=http://www.prx.org/pieces/86736&docid=kbpaK2AwgpEoMM&imgurl=http://s3.amazonaws.com/production.mediajoint.prx.org/public/piece_images/199446/chromosome-t-prx_small.jpg&w=240&h=240&ei=CpjGUPPKIYv0qwGOtoCoBQ&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=8&vpy=366&dur=2350&hovh=192&hovw=192&tx=49&ty=212&sig=106767054772201991398&sqi=2&page=2&tbnh=140&tbnw=144&ndsp=35&ved=1t:429,r:41,s:0,i:67 - The centromeres split. The two chromatids separate. One chromatid moves along the spindle fiber to one end of the cell. The other chromatid moves to opposite end. The cell becomes stretched out as the opposite ends pull apart. Sources http://www.google.com/imgres?hl=en&client=ubuntu&hs=p0a&sa=X&tbo=d&channel=cs&biw=1215&bih=688&tbm=isch&tbnid=HYLaOtN3K5U-WM:&imgrefurl=http://www.sparknotes.com/biology/cellreproduction/mitosis/section3.rhtml&docid=dho-xNTXgTUcPM&imgurl=http://img.sparknotes.com/figures/D/d756b5b73abe2974f3521a828791899f/cytokinesis.gif&w=389&h=399&ei=x5HGUMiYC4mH2AWjoID4Dw&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=4&vpy=144&dur=2962&hovh=227&hovw=222&tx=82&ty=254&sig=106767054772201991398&page=1&tbnh=134&tbnw=131&start=0&ndsp=24&ved=1t:429,r:0,s:0,i:152 - Why do we need DNA replication?? - it insures that each daughter cell will have all of the genetic info it needs to carry out activities - The chromosomes line up across the center of the cell. Each chromosome attaches to a spindle fiber at its centromere, which still holds the chromatin together - molecules of sugar that the two sides of the DNA ladder are made up of alternating between each other Base Pairings - Adenine ----> Thymine - Guanine ----> Cytosine - each doubled rod of condensed chromatin - the cell grows when it doubles in size during the first part of Interphase and makes a copy of its DNA. - The cell is mature when it is fully developed physically and is ready to divide DNA Replication http://www.google.com/imgres?num=10&hl=en&client=ubuntu&tbo=d&channel=cs&biw=1215&bih=688&tbm=isch&tbnid=ZVX7IU7VLMP9YM:&imgrefurl=http://www.dnareplication.info/dnadoublehelix.php&docid=koDmkevb_A9ixM&imgurl=http://www.dnareplication.info/images/dnadoublehelix2.jpg&w=360&h=360&ei=WZnGULnlCsSXrAGS_4DQBQ&zoom=1&iact=hc&vpx=440&vpy=153&dur=7997&hovh=225&hovw=225&tx=93&ty=248&sig=106767054772201991398&sqi=2&page=1&tbnh=150&tbnw=150&start=0&ndsp=30&ved=1t:429,r:3,s:0,i:158 - The chromatin in the nucleus condenses to form chromosomes. Structures called spindle fibers form a platform between the ends of the cell. The nuclear membrane breaks down. Prophase By Madi W. R3 Science