PowerPoint Game Templates
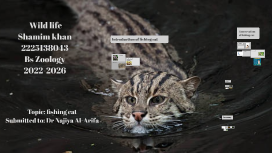
Transcript: Conservation of fishing cat Introduction of fishing cat Health: Fishing cats are susceptible to carnivore protoparvovirus, a disease known to kill them. This disease significantly damages the kidney, spleen and gastrointestinal tract of the body. The fishing cat is also vulnerable to diseases and medical conditions such as feline hemoplasmas, transitional cell carcinoma and canine distemper virus. Conservation Threats Wild life Shamim khan 2225138043 Bs Zoology 2022-2026 Since 2016, the fishing cat is listed as a vulnerable species on the IUCN Red List, as the global population is thought to have declined by around 30% in the years 2010–2015; the destruction of wetlands and killings by local people are major threats to the fishing cat.[1] The destruction of wetlands includes increased pollution or conversion for agricultural use and human settlements. The conversion of mangrove forests to commercial aquaculture ponds is a major threat in Andhra Pradesh, and in some places fishing cats are killed. Over-exploitation of local fish stocks and retaliatory killing by local people are also significant threats. The fishing cat is included on CITES Appendix II and protected by national legislation over most of its range. Hunting is prohibited in Bangladesh, China, India, Indonesia, Myanmar, Nepal, Pakistan, Sri Lanka, and Thailand. Hunting regulations apply in Laos. In Bhutan, Malaysia, and Vietnam, it is not protected outside protected areas, and no information is known about its legal protections in Cambodia. It is the state animal of the Indian state of West Bengal. Its survival depends on protection of wetlands, prevention of indiscriminate trapping, snaring and poisoning. fishing cat The fishing cat (Prionailurus viverrinus) is a medium-sized wild cat of South and Southeast Asia. It has a deep yellowish-grey fur with black lines and spots. Adults have a head-to-body length of 57 to 78 cm (22 to 31 in), with a 20 to 30 cm (8 to 12 in) long tail. Males are larger than females classification of fishing cat: Scientific classification Domain: Eukaryota Kingdom: Animalia Phylum: Chordata Class: Mammalia Order: Carnivora Suborder: Feliformia Family: Felidae Subfamily: Felinae Genus: Prionailurus Species: P. viverrinus Characteristics: The fishing cat has a deep yellowish-grey fur with black lines and spots. Two stripes are on the cheeks, and two are above the eyes running to the neck with broken lines on the forehead. It has two rows of spots around the throat. The spots on the shoulder are longitudinal, and those on the sides, limbs and tail are roundish Endangered in Pakistan: In captivity: Fishing cat captive breeding programmes have been established by the European Association of Zoos and Aquaria and the American Association of Zoos and Aquariums. All the fishing cats kept in zoos around the world are listed in the International Studbook of the World Association of Zoos and Aquariums.Zoos in Thailand house around 30 individuals; birth rates are not particularly high.They have been placed in captivity as an "insurance population" due to their vulnerable status in the wild Taxonomy Topic: fishing cat Submitted to: Dr Najiya Al-Arifa Behaviour and ecology Phylogeny: Distribution and habitat: The fishing cat lives among dense vegetation near water and is thought to be primarily nocturnal. It is known to be a proficient long-distance and underwater swimmer. Adult males and females without dependent young are solitary. Females have been reported to range over areas of 4 to 6 km2 (1.5 to 2.3 sq mi), while males range over 16 to 22 km2 (6.2 to 8.5 sq mi). It has been observed resting in thick grassy habitats, often near a water body but sometimes far away from them. Adults have been recorded to vocalise "chuckling" sounds The fishing cat is broadly but discontinuously distributed in South and Southeast Asia. It predominantly inhabits densely vegetated wetlands around slow-moving bodies of water like swamps and marshes.These include low-salinity bodies such as oxbow lakes, and high-salinity ones such as tidal creeks and mangrove forests. Along these bodies of water, it conceals itself within the thick cover of forests, scrublands, reed beds, and grasslands. Most records are from lowland areas. Reproduction and development: Wild fishing cats most likely mate during January and February; most kittens in the wild were observed in March and April. However, fishing cats may mate as late as June. In captivity, the gestation period lasts 63–70 days; females give birth to an average of two to three kittens; the litter size can be as small as one to as large as four.