electronics presentation
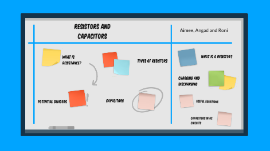
Transcript: Aimee, Angad and Roni Resistors and Capacitors what is resistance? Current is the rate of flow of charged particles what is resistance? Whether resistors are placed in series or parallel affects the total resistance in the circuit ohm's law calculating total resistance of resistors when... 1 ...placed in series 2 ...placed parallel resistors let us introduce precise amounts of resistance into electrical circuits so how do resistors work? what is a resistor? what is a resistor? A wire-wound resistor consists of: A ceramic rod running through the middle with copper wire wrapped around the outside. The number of copper turns controls the resistance: the more copper turns, and the thinner the copper, the higher the resistance. This is due to resistors being affected by three factors... Thermistors, LDRs and diodes are all resistors and also semiconductors. Semiconductors possess the characteristic of higher resistivity than metals. A Ntc thermistor is a resistor whose resistance depends on its temperature. types of resistors LDR - Light Dependent resistor The greater the intensity, the lower the resistance, thus the light provides the energy that releases more electrons. LEDs are designed to let current flow in only the forward bias and require a threshold voltage before they will conduct. In reverse bias, the diode has a very high resistance and very small amounts of current flows. More current leads to an increase in temperature, meaning ‘more electrons have enough energy to escape from their atoms and become charge carriers, leading to a decrease in resistance so the graph curves upwards.’ Led - light emitting diode what is a potential divider? A potential divider is a circuit with a voltage source and resistors in series, where the voltage across the battery is split in the ratio of the resistances.’ Therefore, you can use potential dividers to supply a voltage, V(out), between zero and the battery voltage. potential dividers Alternatively, you can use an LDR or NTC thermistor as a variable resistor in a potential divider A potentiometer is similar to a potential divider, with a variable resistor replacing R(1) and R(2). ‘If you move a slider or turn a knob to adjust the relative sizes of R(1) and R(2), you can vary V(OUT) from zero up to the voltage source.’ the continuously varying resistance of the potentiometer therefore creates an analogue system Capacitors Capacitors Capacitors Capacitors are made up of at least two conducting metallic plates separated by a dielectric Material Capacitance is defined as the amount of charge stored per unit potential difference Q = C V https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=X4EUwTwZ110&t=44s IN series In parallel Dielectric A dielectric is an insulating material which can be slightly polarised within an electric field Charging and discharging Charging and Discharging of a capacitor This exponential function is expressed in terms of RC which is the time constant (T). The duration of charging/ discharging can be divided into 5T for voltage and current analysis. useful equations Charging Discharging Capacitors in AC circuits Capacitors in AC circuits can cause a filtering effect. This can be demonstrated using High pass and Low pass filters. Capacitors in ac circuits High pass Filter High pass Filter A High pass filter allows higher frequency signals to pass through but resists lower range frequencies by reducing it’s amplitude Low pass filter Low pass filter A low pass filter allows lower frequency signals to pass however disrupts higher frequencies in the same manner Warm-up activity bandwidth The range of frequencies a filter allows to pass is known as the bandwidth. Cut off frequency